Laser Removal of Facial Capillaries
Facial capillaries occur due to the widening of capillary lumens deep under the skin, in the dermis. They appear as red or purple lines and spiderweb-like patterns (telangiectasias), and can emerge at any age and in both genders. They are most commonly visible on the nose, around the nostrils, and on the cheeks. The reasons for the appearance of these capillaries are manifold: prolonged sun exposure, skin diseases like rosacea, genetics, hormones, skin aging, or trauma.
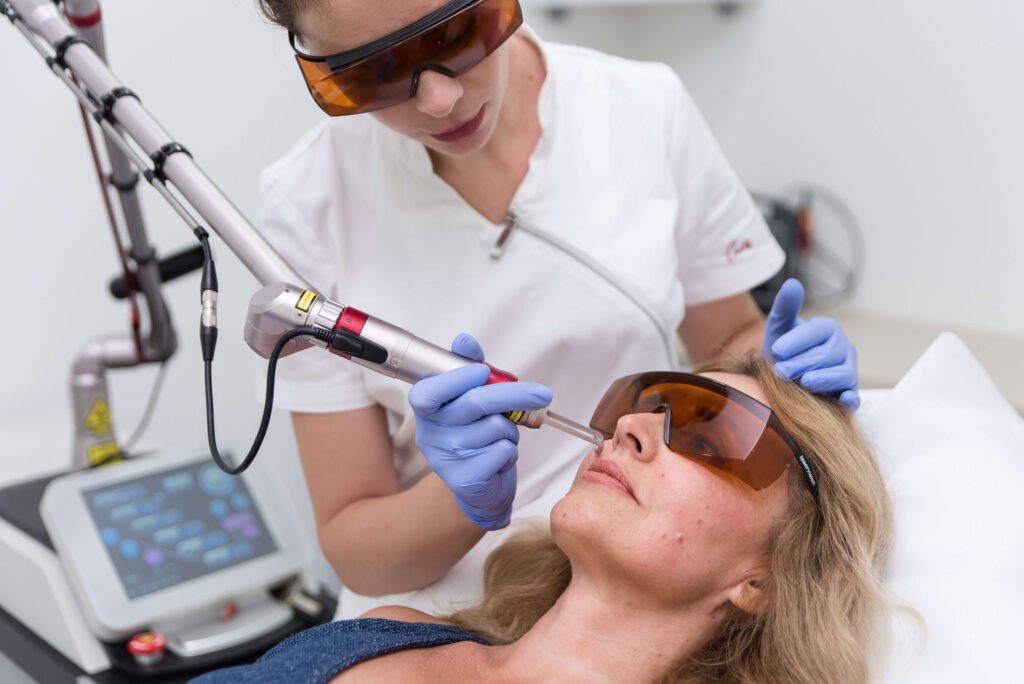
Treatment
The diode laser and Nd-Yag laser for removing capillaries operate on the principle of selective photothermolysis. In this way, energy of a certain wavelength is absorbed in the capillaries, causing their thermal heating, coagulation, and destruction. Since the laser targets the hemoglobin pigment found only in blood vessels, there’s no fear of damaging the surrounding tissue. The treatment is carried out by first cleaning the face of makeup and then cooling the skin before the procedure to make the treatment comfortable. During the treatment, a mild warming sensation and slight stinging can be felt, especially in sensitive areas like the nose region. After treatment, an immediate paleness can be noticed, followed by redness and mild swelling above the capillaries. Within a few days to several weeks, certain capillaries are eliminated and disappear. Capillaries with a diameter ranging from 0.5 to 3 mm can be treated. Laser treatment is not performed during the summer months due to the risk of hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation.
Candidates
If you are troubled by capillaries on your face and want to permanently get rid of them, you are a candidate for laser removal. Candidates do not include pregnant women, epileptics, people taking photosensitive drugs (e.g., isotretinoin, doxycycline), and those who have infections and inflammation in the region they wish to treat.
Results
Smaller spider-like capillaries are completely removed after just one treatment, while more extensive capillaries require 2 to 3 treatments.
Recovery
A few days after the treatment, the treated area may be red and sensitive, and small scabs and mild swelling may appear on the capillary sites. All these symptoms are temporary and transient. Very rare side effects include hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, and scars. However, if post-treatment recommendations are followed, the possibility of these changes occurring is minimized. For the first two to three days, ice can be applied to the treated region to reduce swelling and redness more quickly. It is recommended to apply creams with a high protection factor for a month after the treatment.